Policy Details, Data Retention Dates, and Policy Data Protection Jurisdictions
Policy Details
To aid users' understanding of what policies are "In-Scope" or "Offboarded" for an entity, a new component has been added to the Entity Profile page called Policy Details. This component provides Policy status tracking by displaying the state of all policies applicable to the verified entity and the Policy Status ("In-Scope" or "Offboarded") for each Policy. Whenever a Policy becomes triggered on the entity per scoping rules (and also becomes verified) it is presented within this component as "In Scope"; the Policy is presented within this component as "Offboarded" upon completion of an Offboarding journey for that Policy. Policies cannot be removed from this component once they have been triggered.
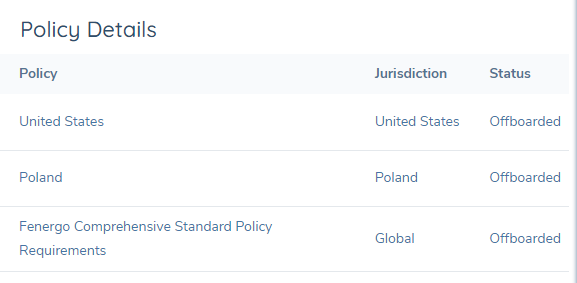
Tracking Data Retention Dates on an Entity
At the completion of an offboarding, the following Data Deletion information is retained against the Entity:
- Data Deletion Process ID ("id")
- Entity ID
- Jurisdiction
- Date of the Offboarding Completion ("initiatedOn")
- Data Retention Period ("dataRetentionPeriodMonths").
- This will be the "Duration in Months" value set during the configuration of the Data Protection Regime.
The system calculates the Data Deletion Date based on the Date of the completed Offboarding and the Data Retention Period. For example, if the Date of the Offboarding Completion was 21/04/2022 and the Data Retention Period was 84 months, the calculated Data Deletion Date would be:
21/04/2022 + 84 months = 21/04/2029
![]()
In the backend, Fenergo SaaS is tracking the statuses of all scoped Jurisdictions for an Entity. Fenergo SaaS can detect what specific Policies have been scoped for the Entity as well as what Policies have been offboarded for an Entity. System logic ensures that offboarded Policies are not picked up in any subsequent Journeys.
Policy Level Data Protection Jurisdictions
As a part of the Data Protection feature, the system will be able to delete specific targeted data from an entity when the corresponding Data Retention date for a given Jurisdiction is reached. While individual policies are generally expected to be siloed by geographic region, it is possible for these policies to extend beyond a single Policy (e.g. an enterprise “EDD” Policy).
Policy configuration allows for the tagging of individual attributes with a Data Protection Jurisdiction value to indicate which jurisdiction’s Data Retention Policy should apply to the individual attribute.
Note: a Data Retention Period for each applicable Jurisdiction should be configured by the user prior to configuring the Data Protection Jurisdiction on the Policy attribute.
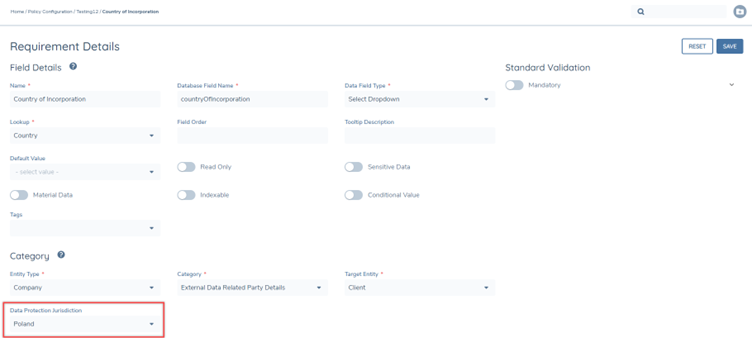
At a Policy level, a user can define the Default Data Protection Jurisdiction. When this attribute has been defined for a Policy, any new attributes added to the Policy will automatically be created with the Data Protection Jurisdiction attribute set to the same value. This will reduce the effort for the configurator and the risk of an attribute being incorrectly tagged.
Note: a Data Retention Period for each applicable Jurisdiction should be configured by the user prior to configuring the Default Data Protection Jurisdiction on the Policy.

A new command has also been introduced at the Policy level that will allow a user to update all attributes within the Policy to align with the value of the Default Data Protection Jurisdiction. This will support clients in updating any existing policies that were created before this feature’s release. The user can initiate this command on any policy in Draft but only after having saved a Default Data Protection Jurisdiction value to the Policy.

- Ensure that the policy is in Draft
- Set the Default Data Protection Jurisdiction value
- Save the Draft
- Press the Refresh button within the Default Data Protection Jurisdiction field to apply the Jurisdiction to all existing attributes in policy
- Save the Draft