Pre Requisites to Running a Data transfer
Creating a Policy
Data transfer using the ETL tool depends on a specific data transfer policy created by the client. These policies represent the data models into which data is transferred and define the structure and fields required by a Fen X client to capture their requirements. Each policy is aligned with a specific geographic jurisdiction.
The policy dictates the data to be transferred and includes validation rules used to ensure the correctness of the data during the data transfer process. When transforming and preparing data for migration, clients can use the structure of the migration policy as a benchmark for data accuracy.
Each column in the uploaded data sources can be mapped to fields in the migration policy. During the validation stage, the mapped data is checked for compliance with the field specifications defined in the policy.
Supported Policy Data Fields
Below are a list of the Data Fields that are currently supported in the migration policy. The product team are looking to extend support for fields that are not supported.
| Data Field | Supported | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Text Field | Yes | |
| Text Area | Yes | |
| Number | Yes | |
| Calculated Number Field | No | |
| Calculated Date Field | No | |
| Calculated Time Period Field | No | |
| Date | Yes | Only specific date formats are supported i.e. dd/mm/yyyy with the date parse transformation applied or ISO 8601 e.g. '1998-03-17T00:00:00.0000000' |
| Data Group | Yes | |
| Select Dropdown | Yes | |
| Multiple Select Dropdown | Yes | Where multiple values need to be transferred seperators should be a pipe, see below |
| Legacy Linked Select Dropdown | Yes | |
| Legacy Linked Multiple Select Dropdown | Yes | |
| Linked Select Dropdown | No | The new v2 Linked lookups cannot be used in the migration policy as they will not pass validation. |
| Linked Multiple Select Dropdown | No | The new v2 Linked Multiple Select lookups cannot be used in the migration policy as they will not pass validation. |
| Legacy Status | No | |
| Search Text Field | No | |
| Status | Yes | Status chips are supported, however the value to apply must be included in the datasource. Conditional values are not applied during the ETL transfer and any updates to the status based on a condition must be happen in journey. |
| Rich Text Editor | No |
Preparing the Data
Before uploading a .CSV file into the ETL tool, it is essential to perform a series of checks and basic data manipulations to ensure compatibility and reduce errors. While the ETL tool can handle some data transformation and included there is some basic checking on the file formats, the following preparatory steps must be completed:
- Handle Blank Values: Where there is no value for a datafield for a particular entity this cell must be left empty, the wording 'NULL' needs to removed. The reason for this is that you can remove a value for an entity by using the word 'NULL' to clear the value in Fen X.
- Standardise Date Fields: Convert all date fields into the required format (e.g., ISO 8601 '1998-03-17T00:00:00.0000000': or DD/MM/YYYY) to enable accurate parsing by the tool. If the date format is DD/MM/YYYY the date transform functionality should be applied in the tool, this is the only date format currently supported by the tool.
- Ensure Unique Column Identifiers: Verify that there are no duplicate column headers in the .CSV file. Each column must have a unique identifier to avoid conflicts during the upload process. This is validated on upload.
- Check Column Headers: Ensure all data columns have corresponding headers. There should be no columns containing data without a defined header or there can be no commas in the header. This is validated on upload.
- Remove Extraneous Rows and Columns: Delete any empty rows below the last row with data to prevent unnecessary processing of blank entries. Remove any empty columns beyond the last column with data to keep the .CSV clean.
- Select Dropdowns: The tool now validates select dropdowns by ensuring that the value defined in the datasource exists within the select drop-down reference list. It also validates multi-select dropdowns and linked dropdowns, confirming the correct parent-child relationship-but only when the legacy linked lookup is used. The new linked dropdowns cannot be used in the migration policy, as they will not pass validation.
- Final Quality Check: Open the .CSV in a text editor or spreadsheet application to check for hidden characters, line breaks, or formatting inconsistencies that may disrupt the upload. i.e. Any text containing special characters like commas, carriage returns, etc., must be enclosed in double quotes (""). If double quotes are used to enclose fields, any double quote appearing inside a field must be escaped by preceding it with another double quote.
- Multi Select Fields: Where the field is a multi-select the values in the datasource should be seperated by a pipe, i.e Ireland|France
- CSV file must be comma seperated: When uploading a .CSV file, it is essential that the file uses a comma (,) as the field separator. This is because our system expects comma-separated values (CSV) to ensure proper parsing and data integrity. However, please be aware that Microsoft Excel uses different default separators based on your regional settings in Windows. For example: In English (United States) regions, the default list separator is a comma. In many European regions (e.g., Germany, France), the default list separator is a semicolon (;). This can cause Excel to generate .CSV files that use semicolons instead of commas, leading to file format issues and the tool will be unable to parse the file. In ETL the file may get stuck on upload or will be uploaded but you will not see the schema when selecting the datasource defnition and no fields will display in the mapping area. You can resolve this by opening the .CSV file using a plain text editor (like Notepad or Notepad++). Check if the fields are separated by semicolons (;).Use Find and Replace to change all ; to ,.Save the file before uploading.
- No special characters in the file name: There should be no special characters or spaces in the file name. This will present an error on upload.
- Field Character Limit: Each field value must not exceed 255 characters. Any value longer than 255 characters will fail on upload. .
Save the file in UTF-8 encoding to prevent character corruption, particularly for special characters or symbols
Unique Identifiers
Unique identifiers are critical for accurate data transfer and management in the ETL process. Each entity being migrated must have a unique identifier to ensure proper tracking and updates. The source system’s unique identifier, is provided by the client and stored in the Fenergo SaaS platform as the ALTERNATEID.
When entities are migrated, the Fenergo SaaS platform also generates its own unique identifier, the FENXID, to further ensure data integrity. However, clients must always supply their own foreign key identifier (the ALTERNATEID) for use during the inital data creation.
- ALTERNATEID: Is derived from the source system’s unique identifier. Stored as the ALTERNATEID in FenX.
- FENXID: The unique identifier generated within FenX.
Client Versus Non Client
Entities created through the ETL process in the "Individual," "Company," or "Other" types can be classified as either Client or Non-Client Entities.
Client Entities are those that have completed the full onboarding process via a Client Onboarding Journey or have been updated through a Maintenance Journey (when using the default Journey Types).
Non-Client Entities are typically created when building an association hierarchy. These Entities exist within Fen-X solely to be part of another Entity’s hierarchy.
Within ETL a flag in the Map System fields called 'IsClient' allows users to set whether the entity is Client or Non Client.' This field must be mapped when creating entities. In the datasource if the data field is set to TRUE for an entity, the entity will be assigned a client role, and the Client chip will display on the entity profile page. When set to FALSE, the entity will be treated as a Non-Client.
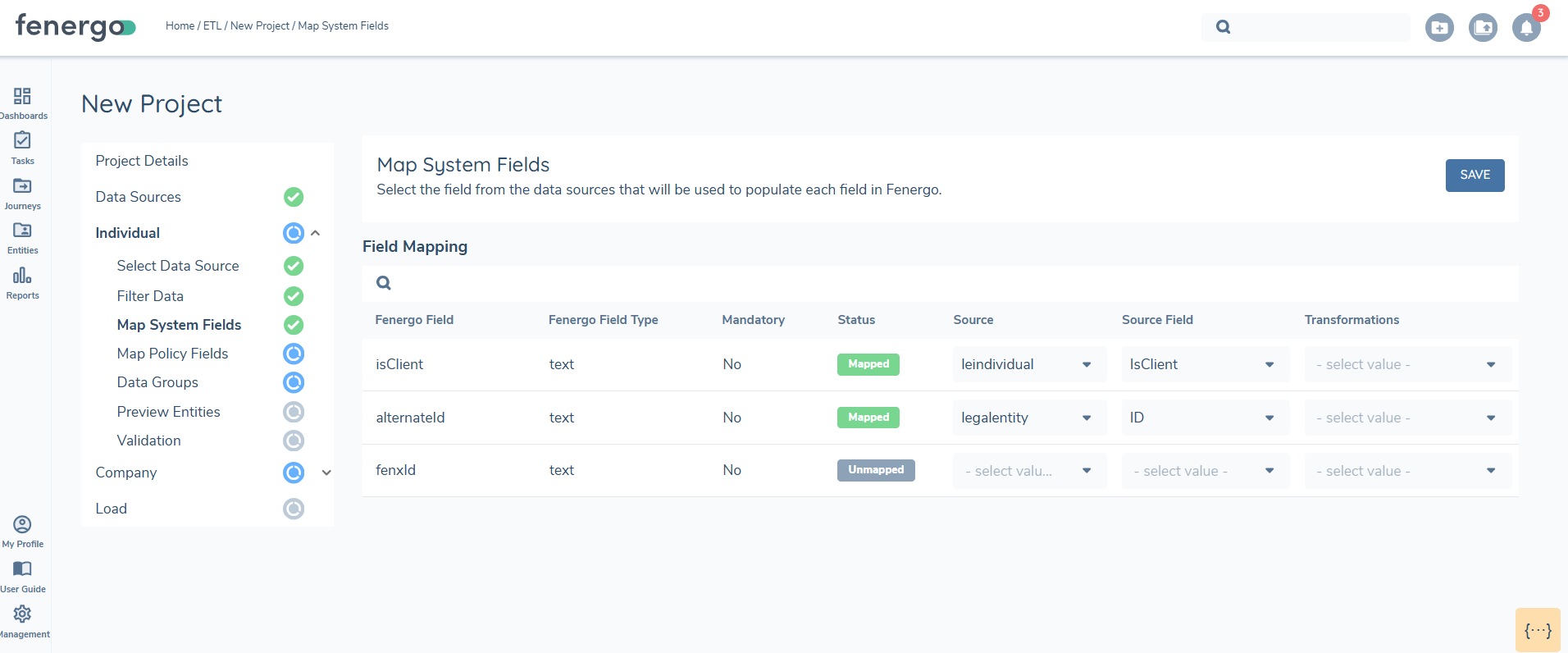
Currently, the ETL process does not distinguish between the requirements for "Client" and "Non-Client" Entities. If clients require fewer data points for their Non-Client Entities, we may introduce the capability to look at Data Requirements with a Target Entity of "Related Party".
This field must be included in the source file and mapped when creating entities so that ETL can determine whether the entity is Client or Non-Client. If not mapped, the Client role will not be set for the entity and the entity is treated as Non Client.
Create Versus Update
Create
When creating entities, the identifier from the source system is saved as the ALTERNATEID in FenX. If the ALTERNATEID exists, the system updates the corresponding record. If it does not exist, a new record is created with the incoming data.
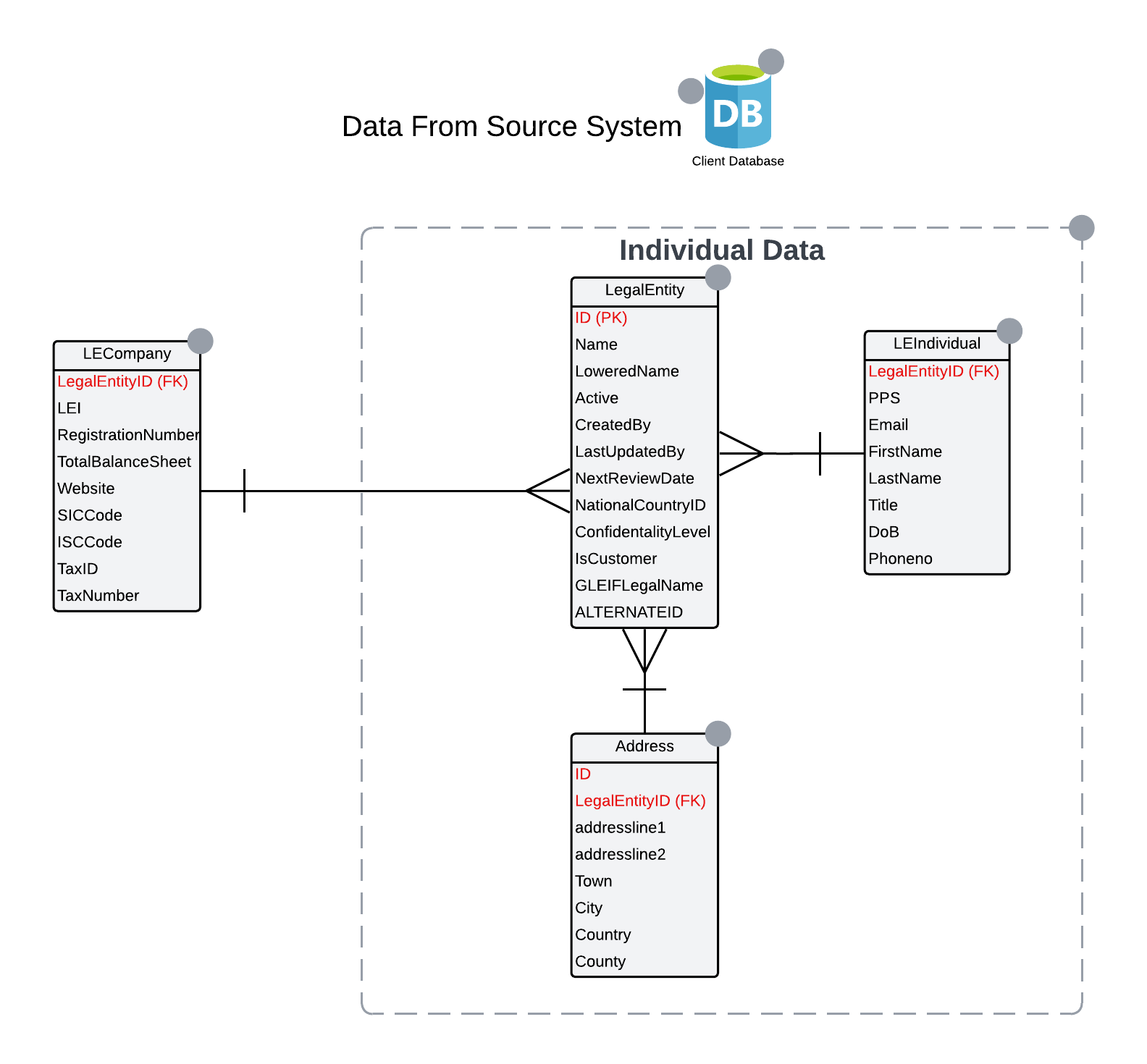
In the above example of data extracted from the source system the LegalEntity.ID is the unique identifier that will be used during entity creation and this will be persisted as the ALTERNATEID in FENX.
Updates
To update an entity, either the FENXID or the ALTERNATEID can be used as the unique identifier, but only one identifier is permitted per ETL project. All operations within a project are consistently aligned to the selected identifier.
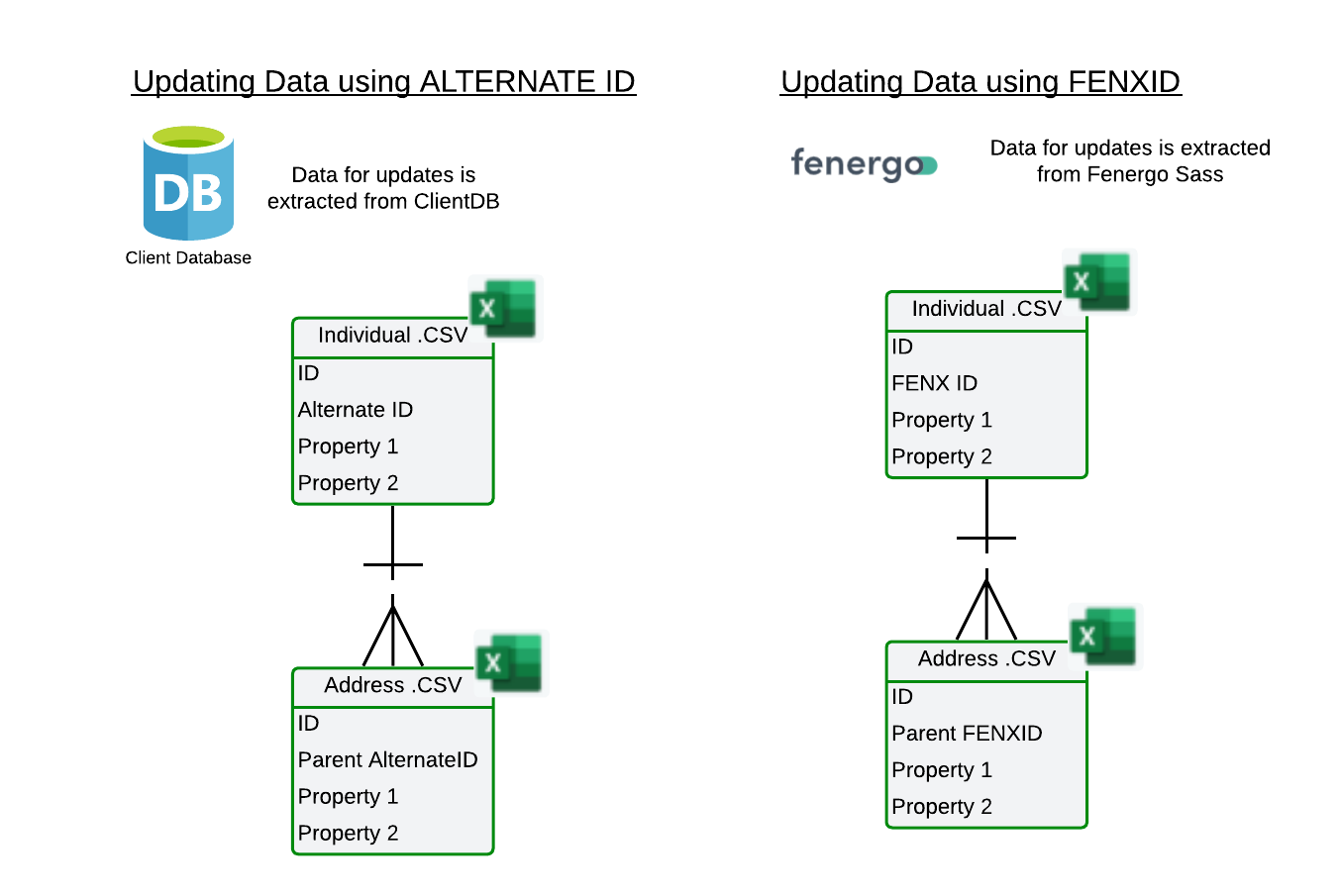
As in the example above. If updates are based on data extracted from the source system, the ALTERNATEID serves as the unique identifier. In this case, data groups would be linked to the entity using the PARENTALTERNATEID.
Conversely, if updates are based on data extracted from FenX, the FENXID would be the unique identifier. Here, the PARENTFENXID would be used to associate the data with the main entity.
When updating an entity, you can perform the following actions:
- Add data to a field
- Update an existing field
- Delete a value from a field
To delete a value from a field, enter NULL in the corresponding cell for the field you want to clear.
Comparisons involving the ALTERNATEID are case-sensitive. This ensures that variations in letter case (e.g., "ABC123" vs. "abc123") are treated as distinct identifiers, if the CASE is different in the unique identifiers it may result in a CREATE instead of an UPDATE
In terms of AlternateID uniqueness, ETL is backward-compatible with the Data migration APIs, meaning if you first used the data migration APIs and then ETL, the AlternateID will be found and the entity updated. However, if you run ETL first and then the data migration APIs, the latter will only maintain uniqueness within the project and therefore won’t find the AlternateID from migrations previously run through ETL and a new entity will be created.
Security - ETL Permissions
User will need the ETL administrator role to see ETL on the left navigation.
| Permission Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ETL Administrator | Ability to access ETL tool, Create and Run migrations | Required by Migration users in lower-level environments to access the ETL configuration. Generally, only provided to Application Support Teams in a Production environment. |